Layer Normalization, and how to compute its Jacobian for Backpropagation?
Step by step implementation in Python
In this regularization technique, we normalize the layer. How do we do that? Let us take a look.
You can download the Jupyter Notebook from here.
Note — This post uses many things from the previous chapters. It is recommended that you have a look at the previous posts.
5.5.1 Layer Normalization, Part I
Suppose we have x,

Then, ‘y’ is

where,

and,

Here, N = 3 because we have 3 entries in x.
We can reduce the normalization function in Python like this

import numpy as np # importing NumPy
np.random.seed(42)def normalize(x): # Normalization
mean = x.mean(axis = 0)
std = x.std(axis = 0)
return (x - mean) / (std + 10**-100)

Now, the most important question is how to compute its derivative/Jacobian?
Similar to the Softmax function, we have a situation like this.

So, the Jacobian ‘J’ for the normalization is

Let us start finding each term in this Jacobian.
Starting with the first term, i.e.,


we know that,

So,


and,

So,

which gives,

Therefore, we have

Now let us calculate the second term, i.e.,


which gives,

After finding every term in the Jacobian, we have a symmetric matrix

We can reduce it like this


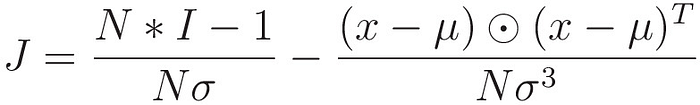
def normalize_dash(x):
N = x.shape[0]
I = np.eye(N)
mean = x.mean(axis = 0)
std = x.std(axis = 0)
return ((N * I - 1) / (N * std + 10**-100)) - (( (x - mean)
.dot((x - mean).T) ) / (N * std**3 + 10**-100))
Let us have a look at an example
x = np.array([[0.2], [0.5], [1.2], [-1.6], [0.5]])
xnormalize(x)normalize_dash(x)normalize_dash(x) == normalize_dash(x).T


We can see that the Normalization Jacobian is symmetric.
We also do scaling and shifting.
By that we mean, We multiply the normalized layer by a scalar and then we add a scalar.
The multiplication scalar is called ‘gamma’ and the addition scalar is called ‘beta’. ‘gamma’ is initialized as ones and ‘beta’ is initialized as ‘zeros’. They are parameters which we will update via some Optimizers.
gamma = np.ones(shape = x.shape) # gamma for scaling
gammabeta = np.zeros(shape = x.shape) # beta for shifting
betascaled_shifted = gamma * normalize(x) + beta
scaled_shifted


I hope you understand now how Normalization works and how to compute the Jacobian for backpropagation. In the next post, we will implement Layer Normalization in ANNs.
If you like this post then please subscribe to my youtube channel neuralthreads and join me on Reddit.
I will be uploading new interactive videos soon on the youtube channel. And I will be happy to help you with any doubt on Reddit.
Many thanks for your support and feedback.
If you like this course, then you can support me at


It would mean a lot to me.
Continue to the next post — 5.5.2 Layer Normalization, Part II.
